Abstract
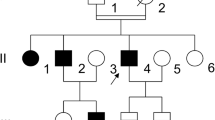
The genetic heterogeneity of severe von Willebrand disease (vWd) type III was estimated by analysing extended haplotypes of eleven intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms and one variable number of tandem repeat polymorphism in 32 patients from 28 families from Germany or of German origin. All patients were screened for gross deletions and for mutations at potential “hot spot” regions of the von Willebrand factor (vWf) gene. Disease-associated haplotypes were established in 24 families. Only a few, apparently unrelated families shared common haplotypes suggesting a considerable genetic heterogeneity in the German population of vWd type III patients. Defects causing vWd type III were identified on 14 out of 56 chromosomes (25%). Gross deletions were detected in two families. A complete homozygous deletion of the vWf gene was displayed in one patient. Another patient was compound heterozygous for a large deletion of at least 100 kb of the vWf gene with an additional, as yet unidentified, defect. One homozygous missense mutation was detected in exon 10, and two non-sense mutations were detected in exon 8 and exon 45 of the vWf gene, respectively. A frameshift mutation (ΔC) in exon 18 was identified in five families and an additional frameshift mutation (ΔG) was found in exon 28 in one family. It appears that ΔC is the most common molecular defect in German patients with vWd type III. Its association with a number of different haplotypes suggests repeated de novo mutations at a mutation “hot spot”. Evidence is presented that particular molecular defects causing vWd type III are associated with different patterns of inheritance, depending on their location within the vWf gene. Complete deletions of the gene and nonsense mutations in the pro-sequence are correlated with recessive inheritance, whereas frameshift and nonsense mutations in the gene sequence corresponding to the mature vWf subunit tend to be inherited in a dominant fashion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anvret M, Blombäck M, Lindstedt M, Söderlind E, Tapper-Persson M, Thelander A-C (1992) Genetic and blood coagulation characterization of “Swedish” families with von Willebrand's disease types I and III: new aspects of heredity. Hum Genet 89: 147–154
Bahnak BR, Lavergne JM, Rothschild C, Meyer D (1991) A stop codon in a patient with severe type III von Willebrand disease [letter]. Blood 78: 1148–1149
Bernardi F, Marchetti G, Bertagnolo V, Faggioli L, Senno L del (1987) Two TaqI RFLPs in the human von Willebrand factor gene. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 1347
Bernardi F, Marchetti G, Guerra S, Casonato A, Gemmati D, Patracchini P, Ballerini G, Conconi F (1990) A de novo and heterozygous gene deletion causing a variant of von Willebrand disease. Blood 75: 677–683
Bird AP (1980) DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic acids Res 8: 1499–1504
Budowle B, Chakraborty R, Giusti AM, Eisenberg AJ, Allen RC (1991) Analysis of the VNTR locus DIS80 by the PCR followed by high resolution PAGE. Am J Hum Genet 48: 137–144
Eikenboom JCJ, Amstel HKP van, Reitsma PH, Briet E (1992) Mutations in severe, type III von Willebrand's disease in the Dutch population: candidate missense and nonsense mutations associated with reduced levels of von Willebrand factor messenger RNA. Thromb Haemost 68: 448–454
Ewerhardt B, Ludwig M, Schwaab R, Schneppenheim R, Olek K (1989) An EcoRI polymorphism in the human von Willebrand factor (vWF) gene. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 5416
Ginsburg D, Bowie EJW (1992) Molecular genetics of von Willebrand disease. Blood 79: 2507–2519
Ginsburg D, Handin RI, Bonthron DT, Donlon TA, Bruns GA, Latt SA, Orkin SH (1985) Human von Willebrand factor (vWF): isolation of complementary DNA (cDNA) clones and chromosomal localization. Science 228: 1401–1406
Iannuzzi MC, Konkle BA, Ginsburg D, Collins FS (1987) RsaI RFLP in the human von Willebrand factor gene. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 5909
Ivy AC, Shapiro PF, Melnick P (1935) The bleeding tendency in jaundice. Surg Gynecol Obstet 60: 781
Konkle BA, Kim S, Iannuzzi MC, Alani R, Collins FS, Ginsburg D (1987) SacI RFLP in the human von Willebrand factor gene. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 6766
Laurell CB (1972) Electroimmunoassay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 124 (Suppl): 21–37
Lavergne JM, Bahnak BR, Verweij CL, Pannekoek H, Meyer D (1987) A second XbaI polymorphic site within the human von Willebrand factor (vWF) gene. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 9099
Lenk H, Nilsson IM, Holmberg L, Weissbach G (1988) Frequency of different types of von Willebrand's disease in the GDR. Acta Med Scand 224: 275–280
Lowe T, Sharefkin J, Yang SQ, Dieffenbach CW (1990) A computer program for selection of oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reactions. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 1757
Lynch DC, Zimmerman TS, Collins CJ, Brown M, Morin MJ, Ling EH, Livingston DM (1985) Molecular cloning of cDNA for human von Willebrand factor: authentication by a new method. Cell 41: 49–56
MacFarlane DE, Stibbe J, Kirby EP, Zucker MB, Grant RA, McPherson J (1975) Letter: a method for assaying von Willebrand factor (ristocetin cofactor). Thromb Diathes Haemorrh 34: 306–308
Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield LA, Worrall NK, Shelton Inloes BB, Sorace JM, Alevy YG, Sadler JE (1989) Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 264: 19514–19527
Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield LA, Lester Mancuso TL, Le Beau MM, Sorace JM, Sadler JE (1991) Human von Willebrand factor gene and pseudogene: structural analysis and differentiation by polymerase chain reaction. Biochemistry 30: 253–269
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Mannucci PM, Bloom AL, Larrieu MJ, Nilsson IM, West RR (1984) Atherosclerosis and von Willebrand factor I. Prevalence of severe von Willebrand's disease in western Europe and Israel. Br J Haematol 57: 163–169
Mazurier C, Parquet Gernez A, Goudemand M (1977) Enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay of factor VIII-related antigen. Interest in study of von Willebrand's disease. Pathol Biol (Paris) 25 Suppl: 18–24
Merles G, Ludwig M, Schwaab R, Brackmann HH, Olek K (1993) ΔC in exon 18 of the von Willebrand gene is uncommon in German vWd type III patients (letter). Thromb Haemost 70: 1064–1065
Mielke CHJ, Kaneshiro MM, Maher JA, Weiner JM, Rapaport SJ (1969) The standardized normal bleeding time and its prolongation by aspirin. Blood 34: 204–215
Ngo KY, Glotz VT, Koziol JA, Lynch DC, Gitschier J, Ranieri P, Ciavarella N, Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS (1988) Homozygous and heterozygous deletions of the von Willebrand factor gene in patients and carriers of severe von Willebrand disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2753–2757
Nishino K, Lynch DC (1986) A polymorphism of the human von Willebrand factor (vWf) gene with BamHI. Nucleic Acids Res 14: 4697
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T (1989) Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel elecrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2766–2770
Peake IR, Liddell MB, Moodie P, Standen G, Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield LA, Sorace JM, Sadler JE, Verweij CL, Bloom AL (1990a) Severe type III von Willebrand's disease caused by deletion of exon 42 of the von Willebrand factor gene: family studies that identify carriers of the condition and a compound heterozygous individual. Blood 75: 654–661
Peake IR, Bowen D, Bignell P, Liddell MB, Sadler JE, Standen G, Bloom AL (1990b) Family studies and prenatal diagnosis in severe von Willebrand disease by polymerase chain reaction amplification of a variable number tandem repeat region of the von Willebrand factor gene. Blood 76: 555–561
Quadt R, Verweij CL, Vries CJ de, Briet E, Pannekoek H (1986) A polymorphic XbaI site within the human von Willebrand factor (vWF) gene identified by a vWF cDNA clone. Nucleic Acids Res 14: 7139
Ruggeri ZM, Ware J (1992) The structure and function of von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost 67: 594–599
Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS (1981) The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood 57: 1140–1143
Sadler JE (1994) A revised classification of von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemost 71: 520–525
Sadler JE, Shelton Inloes BB, Sorace JM, Harlan JM, Titani K, Davie EW (1985) Cloning and characterization of two cDNAs coding for human von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 6394–6398
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239: 487–491
Schneppenheim R, Plendl H, Budde U (1988) Luminography — an alternative assay for detection of von Willebrand factor multimers. Thromb Haemost 60: 133–136
Shelton Inloes BB, Chehab FF, Mannucci PM, Federici AB, Sadler JE (1987) Gene deletions correlate with the development of alloantibodies in von Willebrand disease. J Clin Invest 79: 1459–1465
Verweij CL, Vries CJ de, Distel B, Zonneveld AJ van, Kessel AG van, Mourik JA van, Pannekoek H (1985) Construction of cDNA coding for human von Willebrand factor using antibody probes for colony-screening and mapping of the chromosomal gene. Nucleic Acids Res 13: 4699–4717
Wahlberg TB, Blomback M, Ruggeri ZM (1983) Differences between heterozygous dominant and recessive von Willebrand's disease type I expressed by bleeding symptoms and combinations of factor VIII variables. Thromb Haemost 50: 864–868
Weiss HJ, Ball AP, Mannucci PM (1982) Incidence of severe von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med 307: 127
Zhang ZP, Lindstedt M, Falk G, Blomback M, Egberg N, Anvret M (1992a) Nonsense mutations of the von Willebrand factor gene in patients with von Willebrand disease type III and type I. Am J Hum Genet 51: 850–858
Zhang ZP, Falk G, Blomback M, Egberg N, Anvret M (1992b) A single cytosine deletion in exon 18 of the von Willebrand factor gene is the most common mutation in Swedish vWD type III patients. Hum Mol Genet 1: 767–768
Zielenski J, Rozmahel R, Bozon D, Kerem B, Grzelczak Z, Riordan JR, Rommens J, Tsui LC (1991) Genomic DNA sequence of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Genomics 10: 214–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneppenheim, R., Krey, S., Bergmann, F. et al. Genetic heterogeneity of severe von Willebrand disease type III in the German population. Hum Genet 94, 640–652 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206958
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206958