Abstract
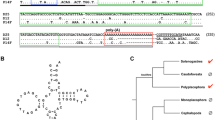
We have characterized a highly repetitive family, named Hy/Pol III, in the genome of the European salamanders Hydromantes (Plethodontidae). This family consists of short, tandemly repeated sequences organized in clusters, scattered through the genome as shown both by in situ hybridization to chromosomes and by Southern blot hybridization. The repeat unit is about 200 by in length and it is a composite element since it contains a SINE-like retroposon with a tRNA structure, flanked by two short direct repeats. The whole element itself is bordered by two other direct repeats. The sequence data suggest that two elements, presumably derived from polymerase III transcripts, have been inserted one into the other, giving rise to the observed composite structure. During evolution the Hy/Pol III family was then amplified by tandem duplication at the DNA level. The inferred relationships between Hy/Pol III members from three representative species of the European Hydromantes suggests that a subfamily structure characterizes the evolutionary history of this family.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman EJ (1983) Molecular cloning and sequencing of OAX DNA: an abundant gene family transcribed and activated in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J 2:1417–1422
Batistoni R, Nardi I, Rebecchi L, Nardone M, Demartis A (1991) A centromeric satellite DNA in the European plethodontid salamanders (Amphibia, Urodela). Genome 34:1007–1012
Batistoni R, Marracci S, Cardelli M, Nardi I (1992) Two interspersed repetitive DNA elements in the genome of the European plethodontid salamanders (Amphibia, Urodela). Atti Assoc Genet Ital 38:149
Calabretta B, Robberson DL, Barrera-Saldana HA, Lambrou TO, Saunders GF (1982) Genome instability in a region of human DNA enriched in Alu repeat sequences. Nature 296:219–225
Chalker DL, Sandmeyer SB (1992) Ty3 integrates within the region of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation. Genes Dev 6:117–128
Craigie R (1992) Hotspots and warmspots: integration specificity of retroelements. Trends Genet 8:187–189
Deininger PL, Batzer MA, Hutchison CA, Edgell MH (1992) Master genes in mammalian repetitive DNA amplification. Trends Gent 8:307–311
Dover GA (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Dover GA (1986) Molecular drive in multigene families: how biological novelties arise, spread and are assimilated. Trends Genet 2:159–165
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package). Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Finnegan DJ (1992) Transposable elements. Cuff Opin Genet Dev 2:861–867
GCG, Genetics Computer Group (1993) Program manual for the GCG Package. 575 Science Drive, Madison, WI, 53711
Granbastien MA (1992) Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet 8:103–108
Kido Y, Aono M, Yamaki T, et al. (1991) Shaping and reshaping of salmonid genomes by amplification of tRNA-derived retroposons during evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2326–2330
Krane DE, Andrew GC, Cheng JF, Hardison RC (1991) Subfamily relationships and clustering of rabbit C repeats. Mol Biol Evol 8:1–30
Jeffreys AJ, Flavell RA (1977) A physical map of the DNA flanking the rabbit β-globin gene. Cell 12:429–439
Ji H, Moore DP, Blomberg MA, et al. (1993) Hotspots for unselected Ty1 transposition events on yeast chromosome III are near tRNA genes and LTR sequences. Cell 73:1007–1018
Jurka J (1989) Subfamily structure and evolution of the human L1 family of repetitive sequences. J Mol Evol 29:496–503
Lanave C, Pesole G (1993) Stationary Markov Processes in the evolution of biological macromolecules. Binary 5:191–194
Lanave C, Preparata G, Saccone C, Serio G (1984) A new method for calculating evolutionary substitution rates. J Mol Evol 20:86–93
Lanza B (1983) Ipotesi sulle origini del popolamento erpetologico della Sardegna. Lav Soc Ital Biogeogr 8:723–744
Lanza B, Caputo V, Nascetti G, Bullini L (1994) Morphologic and genetic studies on the European plethodontid salamanders: taxonomic inferences. Monogr Museo Reg Sci Nat (Torino), in press
Martin SL (1991) LINES. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1:505–508
McDonald J (1993) Evolution and consequences of transposable elements. Curr Opin Genet Dev 3:855–864
Meyerhof W, Witting B, Tappeser B, Knochel W (1987) Transcription termination and processing of transcripts from tRNA-related Xenopus satellite DNA sequences. Eur J Biochem 164:287–293
Minghetti PP, Dugaiczyk A (1993) The emergence of new DNA repeats and the divergence of primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1872–1876
Mizuno S, Macgregor HC (1974) Chromosomes, DNA sequences, and evolution in salamanders of the genus Plethodon. Chromosoma 48:239–296
Nagahashi S, Endoh H, Suzuki Y, Okada N (1991) Characterization of a tandemly repeated DNA sequence family originally derived by retroposition of tRNAGlu in the newt. J Mol Biol 222:391–404
Nardi I (1991) Cytogenetics of the European plethodontid salamanders, genus Hydromantes. In: Green DM, Sessions SK (eds) Amphibian cytogenetics and evolution. Academic Press, Jovanovich HB, pp 131–156
Okada N (1991a) SINEs. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1:498–504
Okada N (1991b) SINEs: Short interspersed repeated elements of the eukaryotic genome. Trends Ecol Evol 6:358–361
Pascale E, Liu C, Valle E, Usdin K, Furano AV (1993) The evolution of long interspersed repeated DNA (L1, LINE 1) as revealed by the analysis of an ancient rodent L1 DNA family. J Mol Evol 36:9–20
Pryciak PM, Varmus HE (1992) Nucleosomes, DNA-binding proteins, and DNA sequence modulate retroviral integration target site selection. Cell 69:769–780
Quentin Y (1992) Fusion of a free left Alu monomer and a free right Alu monomer at the origin of the Alu family in the primate genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 20:487–493
Saccone C, Lanave C, Pesole G, Preparata G (1990) Influence of base composition on quantitative estimates of gene evolution. In: Doolittle RF (ed) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, Jovanovich HB, vol 183, pp 570–583
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Smith HM, Wake, DB (1993) Hydromantes Gistel, 1848 (Amphibia, Caudata). Proposed designation of Salamandra genei Temminck and Schlegel, 1838 as the type species. Bull Zool Nomen case 2868, in press
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Tautz D, Renz M (1983) An optimized freeze-squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem 132:14–19
Traboni C, Ciliberto G, Cortese R (1982) A novel method for site-directed mutagenesis: its application to a eukaryotic tRNAPro gene promoter. EMBO J 1:415–420
Voytas DF, Boeke JD (1993) Yeast retrotransposons and tRNAs. Trends Genet 9:421–426
Wake DB (1993) Phylogenetic and taxonomic issues relating to salamanders of the family plethodomidae. Herpetologica 49:229–237
Zharkikh A, Li WH (1992) Statistical properties of bootstrap estimation of phylogenetic variability from nucleotide sequences. I. Four taxa with a molecular clock. Mol Biol Evol 9:1119–1147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: R. Batistoni
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batistoni, R., Pesole, G., Marracci, S. et al. A tandemly repeated DNA family originated from SINE-related elements in the European plethodontid salamanders (Amphibia, Urodela). J Mol Evol 40, 608–615 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160508
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160508