Abstract
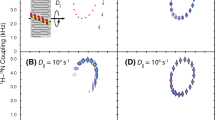
Model-membrane systems composed of liquid-crystalline bicellar phases can be uniaxially oriented with respect to a magnetic field, thereby facilitating structural and dynamics studies of membrane-associated proteins. Here we quantitatively characterize a method that allows the manipulation of the direction of this uniaxial orientation. Bicelles formed from DMPC/DHPC are examined by 31P NMR under variable-angle sample-spinning (VAS) conditions, confirming that the orientation of the liquid-crystalline director can be influenced by sample spinning. The director is perpendicular to the rotation axis when Θ (the angle between the sample-spinning axis and the magnetic field direction) is smaller than the magic angle, and is parallel to the rotation axis when Θ is larger than the magic angle. The new 31P NMR VAS data presented are considerably more sensitive to the orientation of the bicelle than earlier 2H studies and the analysis of the sideband pattern allows the determination of the orientation of the liquid-crystal director and its variation over the sample, i.e., the mosaic spread. Under VAS, the mosaic spread is small if Θ deviates significantly from the magic angle but becomes very large at the magic angle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayle, J.P., Perez, F. and Courtieu, J. (1988) Liq. Cryst., 3, 753-758.
Cheng, V.B., Suzukawa, H.H. and Wolfsberg, M. (1973) J. Chem. Phys., 59, 3992-3999.
Courtieu, J., Alderman, D.W., Grant, D.M. and Bayles, J.P. (1982) J. Chem. Phys., 77, 723-730.
Courtieu, J., Bayle, J.P. and Fung, B.M. (1994) Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc., 26, 141-169.
Dufourc, E.J., Mayer, C., Stohrer, J., Althoff, G. and Kothe, G. (1992) Biophys. J., 61, 42-57.
Gaemers, S. and Bax, A. (2001) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123, 12343-12352.
Glaubitz, C. and Watts, A. (1998) J. Magn. Reson., 130, 305-316.
Glover, K.J., Whiles, J.A., Wood, M.J., Melacini, G., Komives, E.A. and Vold, R.R. (2001) Biochemistry, 40, 13137-13142.
Hediger, S., Signer, P., Tomaselli, M., Ernst, R.R. and Meier, B.H. (1997) J. Magn. Reson., 125, 291-301.
Howard, K.P. and Opella, S.J. (1996) J. Magn. Reson. Ser., B112, 91-94.
Kohler, S.J. and Klein, M.P. (1977) Biochemistry, 16, 519-526.
Losonczi, J.A. and Prestegard, J.H. (1998) Biochemistry, 37, 706-716.
Marassi, F.M., Opella, S.J., Juvvadi, P. and Merrifield, R.B. (1999) Biophys. J., 77, 3152-3155.
Mehring, M. (1983) Principles of High Resolution NMR in Solids, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Moll, F. and Cross, T.A. (1990) Biophys. J., 57, 351-362.
Nieh, M.P., Glinka, C.J., Krueger, S., Prosser, R.S. and Katsaras, J. (2001) Langmuir, 17, 2629-2638.
Nieh, M.P., Glinka, C.J., Krueger, S., Prosser, R.S. and Katsaras, J. (2002) Biophys. J., 82, 2487-2498.
Picard, F., Paquet, M.J., Levesque, J., Belanger, A. and Auger, M. (1999) Biophys. J., 77, 888-902.
Prosser, R.S., Hwang, J.S. and Vold, R.R. (1998) Biophys. J., 74, 2405-2418.
Sanders, C.R. and Landis, G.C. (1995) Biochemistry, 34, 4030-4040.
Sanders, C.R. and Schwonek, J.P. (1992) Biochemistry, 31, 8898-8905.
Sanders, C.R., Hare, B.J., Howard, K.P. and Prestegard, J.H. (1994) Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc., 26, 421-444.
Saupe, A. (1964) Z. Naturforsch., 19a, 161-171.
Seelig, J. (1978) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 515, 105-140.
Smith, S.A., Levante, T.O., Meier, B.H. and Ernst, R.R. (1994) J. Magn. Reson. Ser., A106, 75-105.
Struppe, J., Komives, E.A., Taylor, S.S. and Vold, R.R. (1998) Biochemistry, 37, 15523-15527.
Tian, F., Losonczi, J.A., Fischer, M.W.F. and Prestegard, J.H. (1999) J. Biomol. NMR, 15, 145-150.
Vold, R.R. and Prosser, R.S. (1996) J. Magn. Reson. Ser., B113, 267-271.
Zandomeneghi, G., Tomaselli, M., Van Beek, J.D. and Meier, B.H. (2001) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123, 910-913.
Zandomeneghi, G., Williams, P.T.F., Hunkeler, A. and Meier, B.H. (2003) J. Biomol. NMR, 25, 125-132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zandomeneghi, G., Tomaselli, M., Williamson, P.T. et al. NMR of bicelles: orientation and mosaic spread of the liquid-crystal director under sample rotation. J Biomol NMR 25, 113–123 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022236217018
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022236217018